The New Order of AI Generative Development: Deconstructing the Vibe Coding Ecosystem
Vibe Coding is an early-stage project with clear structural growth, strong potential for platform moat, and diverse, scalable application scenarios.
Vibe Coding is an early-stage track with clear structural growth, multi-scenario scalability, and strong platform moat potential. What it drives is not only the evolution of development tools, but also a redistribution of building rights and a universal release of creativity.
In the early days of computer development, programming was a highly abstract and closed activity. Developers had to directly operate assembly language or even binary, inputting programs via punch cards, tapes, or terminal commands, lacking visual interfaces and real-time feedback, making trial and error extremely costly. Early programming was mainly in the hands of engineers in scientific research or military systems, with ordinary people having almost no access. In the 1980s, with the popularization of personal computers and the development of high-level languages such as BASIC and C, programming gradually acquired an enlightening attribute. At that time, learners taught themselves to write utility programs or simple animations through command lines and paper tutorials, but to truly build a runnable system still required mastering underlying knowledge such as memory management and file system operations, and the threshold for deployment and dissemination remained high.
Although the LAMP architecture composed of HTML, PHP, and JavaScript later brought a certain degree of democratization to development, and open-source tools such as Discuz and WordPress enabled faster implementation of forums and blogs, the entire development process still relied on professional skills and engineering cognition.
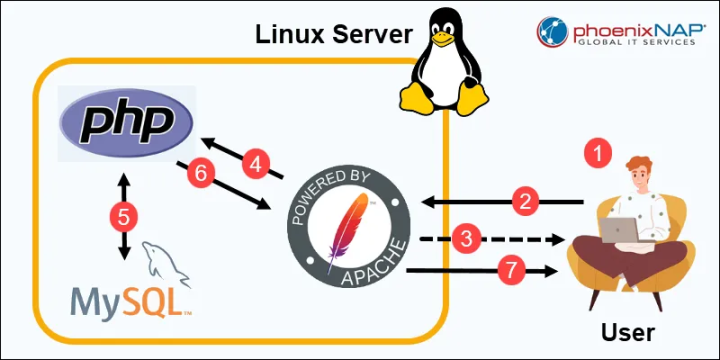
Even in the era of Web2 and mobile development, although the modern tech stack is more powerful, the development path has become more complex, involving a complete chain from design tools (such as Figma) to front-end and back-end frameworks (such as React, Node.js), and then to cloud deployment and third-party service integration, making it still difficult for non-professional users to complete independently.
On the surface, the development process is constantly evolving towards standardization and high efficiency, but the technical threshold has never truly disappeared. The right to build is still concentrated in the hands of a few who master the knowledge and tools.
The AIGC Era: Coexistence of Dawn and Dilemma in Programming
Generative AI has been widely applied, once again greatly lowering the threshold for programming.
With breakthroughs in semantic understanding, code generation, and context retention by large models such as GPT-4, Claude 3, and Gemini, development behavior has, for the first time, shifted from "structural understanding" to "perceptual dialogue." We see that people can communicate intentions directly with the system through natural language, allowing AI to generate required functions, interfaces, components, or even complete pages. Prompt has become the new input method, and system responses have upgraded from suggested fragments to structured, composable results.

AIGC not only improves development efficiency but also breaks the "language barrier." More and more non-programmers are beginning to use Copilot-like tools to complete code, debug logic, write interfaces, and even quickly finish web prototypes or function simulations based on ChatGPT. The potential of AIGC programming is initially emerging at this stage: code becomes "conversational," and development becomes "co-creative."
Of course, the first wave of this transformation has also exposed many limitations:
Most generative models are still at the "fragment generation" level, unable to understand the full scope of tasks, let alone organize complex project structures across files and modules;
Code output lacks context memory, and generated results are often not reusable or require a lot of manual correction;
Lack of connection to the runtime environment, so generated code often cannot be directly deployed, tested, or launched;
Almost all AIGC tools are designed around "helping developers write code faster," rather than "empowering people who can't code with building rights."
Especially in the world of Copilot, developers become more efficient, but non-developers still cannot enter the game.
Although AIGC programming has significantly improved development efficiency and lowered the language barrier, it still mainly revolves around existing developers, and building capabilities have not yet truly reached a broader population. Against this backdrop, a new generative paradigm, Vibe Coding, is emerging, attempting to bypass engineering barriers and open a new chapter in programming equality.
Vibe Coding: The Next Stage of Generative Building Paradigm
Vibe Coding is a hot term in the tech field recently, considered a new trend in the AIGC programming field, attempting to reconstruct the logical starting point of the entire application building process. According to IBM's technical interpretation, Vibe Coding is defined as a programming model that uses natural language input as the main interaction method. Users express development goals through colloquial descriptions, and the system uses large models to assist in generating code, organizing logical structures, and outputting runnable products. Such systems attempt to identify building intentions from input semantics and transform them into composable, deployable, and testable structural results.
Unlike traditional Copilot-like AI tools, Vibe Coding represents a "building rights delivery mechanism" for a broader audience, especially non-engineering background users. Its core is not to make users understand code better, but to allow users to fully describe, trial, publish, and repeatedly iterate their product structure without understanding code.
In fact, this trend has significantly heated up since 2025.
We see platforms like Cursor taking the lead in introducing the "conversational building" concept into IDE systems, supporting natural language control of project structure, cross-file code generation, and instant running previews. More platforms are beginning to design development processes around the path from "Prompt to module to publishing," attempting to create a semantic-driven application creation closed loop.
Beyond the technical path, Vibe Coding also represents a brand-new product organization paradigm: it emphasizes rapid prototyping, lightweight iteration, high reuse, and distributability, adapting to fragmented application scenarios such as creator economy, community operations, and individual entrepreneurship, becoming an important generative method for the next generation of lightweight Web3 applications or interactive content.
Typical Representatives of the Vibe Coding Track
With the development of the Vibe Coding trend, more and more projects are currently trying to productize around this paradigm, gradually deriving multiple paths and solutions.
In this field, projects such as Infinity Ground, Ohara AI, and Dev.fun have gradually emerged as representative explorers in the current Vibe Coding track. Next, we will break down the capability positioning, user paths, and building closed loops of these three types of platforms one by one, and try to outline a preliminary map of the Vibe Coding industry.
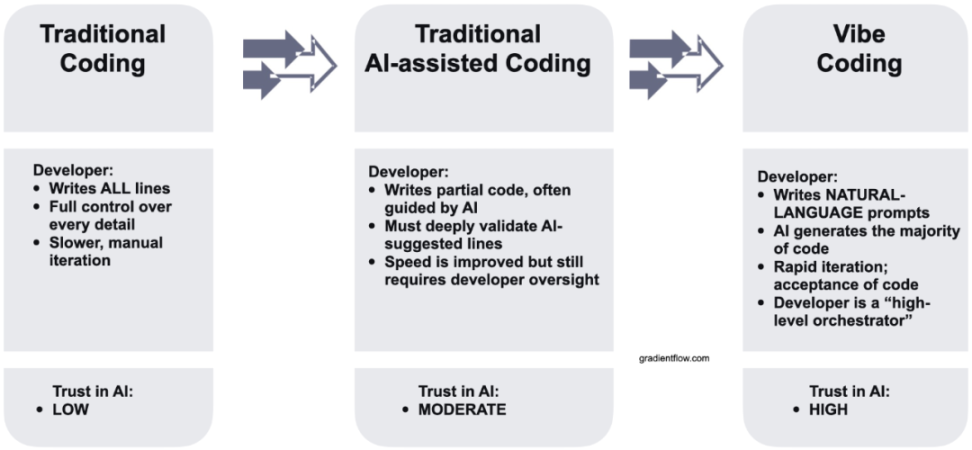
It should be noted that tool-type products that focus on IDE enhancement and localized programming assistants, such as Cursor, Codeium, Windsurf, etc., are mostly embedded in the local programming environment familiar to developers, focusing on code completion, cross-file generation, context linkage, and other process optimizations, significantly improving the development efficiency of existing engineers.
However, the core design of such products is still to "improve programmer efficiency," not to "empower non-programmers to build completely." Their interaction mode still relies on code editors and engineering semantics, so they have not changed the underlying logic of development and are difficult to deliver "end-to-end" applications outside the IDE framework, and also lack some Web3 features. Based on this, these platforms are not included in this comparison.
- Infinity Ground
Infinity Ground is one of the most representative projects in the current Vibe Coding track, dedicated to providing a natural language-driven building path for users without an engineering background.
This project is positioned as a Web3 building platform for ordinary creators, content operators, and individual developers. Its core goal is to compress the development process from "intention to product" into an understandable, operable, and launchable closed-loop path, thereby creating a decentralized "Web3 App Store."
One of the main features of the Infinity Ground platform is the full-process natural language drive. In this system, users can describe target functions through Prompts, and the system will automatically call component libraries, logic modules, and page templates to generate complete application content, including front-end pages, business logic, and on-chain interfaces. The generated results are packaged as accessible links and deployed online directly, without the need for code writing or environment configuration. The new process skips the IDE environment, joint debugging and deployment, and back-end on-chain integration processes relied on by traditional development, greatly reducing the application building threshold.

In terms of interaction, Infinity Ground introduces the Agentic programming paradigm, supporting rapid generation of functional modules from semantics through task decomposition, context understanding, and model strategy routing. The platform supports multi-model collaboration (such as GPT-4 and Claude), dynamic parameter optimization, structured output, and interpretable result generation, enhancing the controllability and comprehensibility of non-technical users during the interaction process.
According to user prompt requirements, applications can support wallet connection, permission management, and payment interfaces, with complete Web3 usage characteristics. The platform also supports users to distribute applications to communities, social platforms, or other channels in the form of links, forming an outward path from building to use and then to dissemination. The entire process is self-contained and complete, and users can complete delivery without leaving the platform.
In addition to page building and interaction configuration, Infinity Ground is also the first among similar platforms to enable semantic generation of smart contracts, becoming an important explorer of on-chain logic generation in the context of Vibe Coding. The platform has built-in contract generation and deployment modules, allowing users to complete a series of smart contract generation, packaging, and on-chain operations, including Airdrop and Token creation, simply by describing in natural language, such as "create a token airdrop with 1000 recipients," without touching the Solidity programming language or performing local compilation or environment configuration.
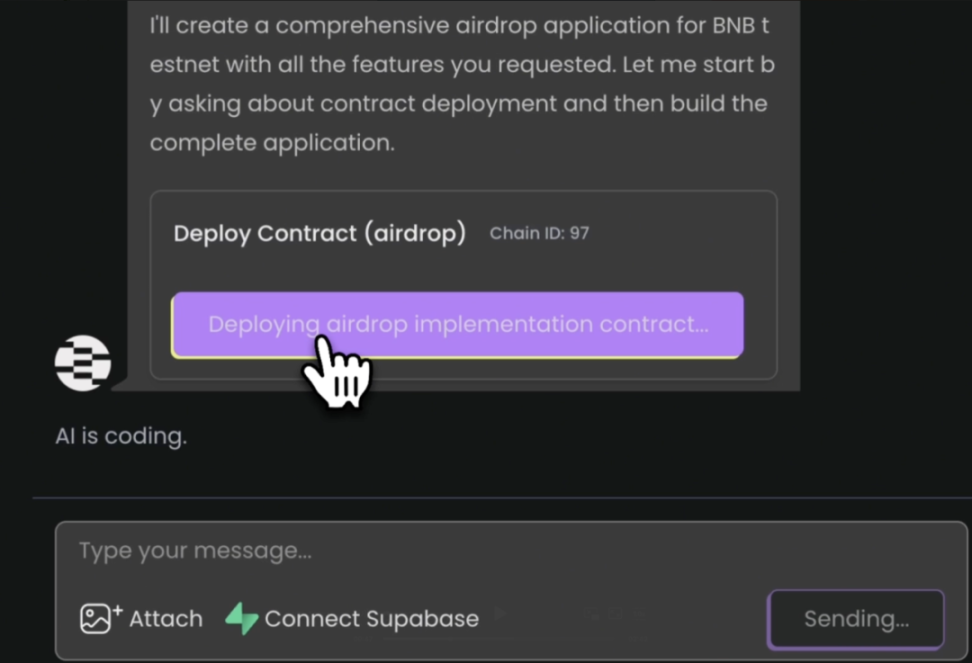
To ensure security and contract usability, the system's preset templates all come from third-party standard contract libraries that have undergone security audits and encapsulate necessary parameter configurations and permission control logic. After the user inputs the target at the semantic level, the platform will call the corresponding template and complete the deployment and execution, ensuring that the building path is both low-threshold and has on-chain stability and traceability.
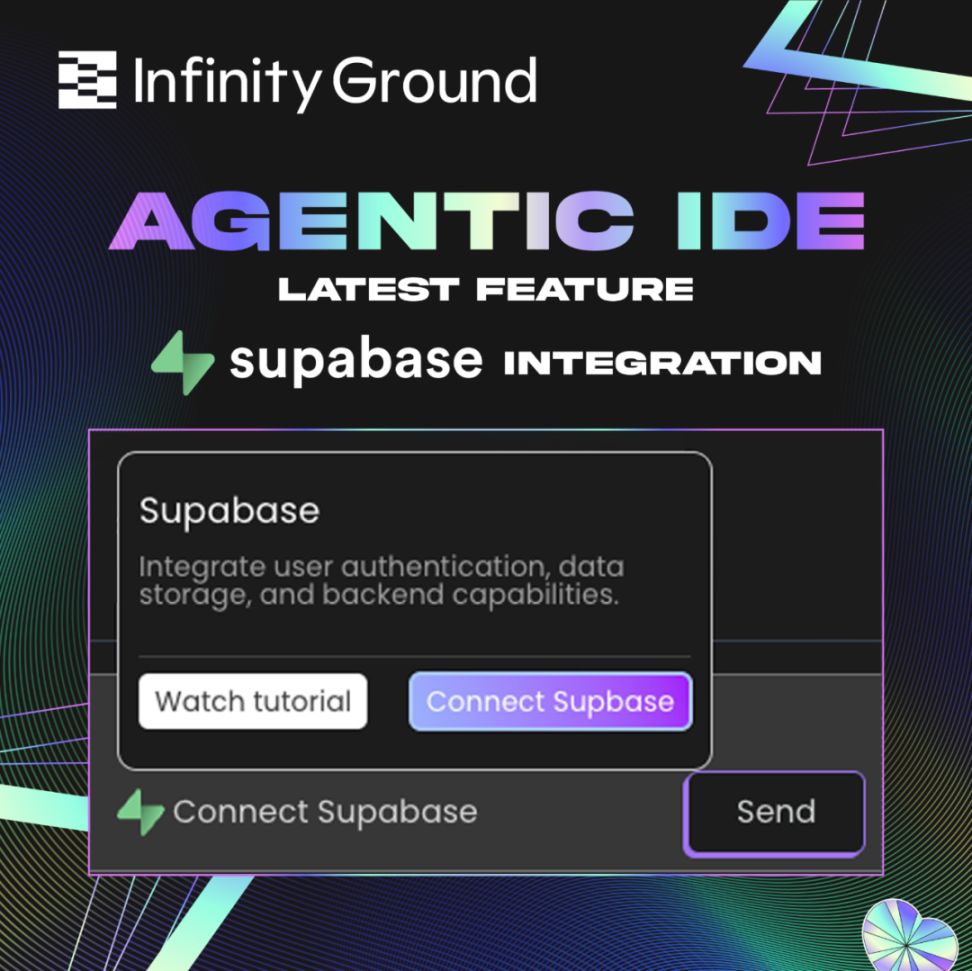
It is worth noting that the platform also provides background monitoring and data tracking functions for contract behavior, helping users observe on-chain indicators such as call frequency, interactive wallet distribution, and token flow paths. This integrated capability of "generatable + deployable + maintainable" greatly enhances the operability of on-chain logic for users without an engineering background, and also builds a technical moat for the platform from "buildable" to "runnable."
On this basis, Infinity Ground has further established a template library, building leaderboard, and code Remix system, supporting users to perform secondary generation based on existing templates or upload custom modules, gradually forming a supply-side building network. The platform also introduces blockchain-based template version control, decentralized incentive mechanisms, and contribution revenue distribution paths. Users can be rewarded by contributing templates and improving the building process, building a production closed loop around AI collaboration and user co-construction.
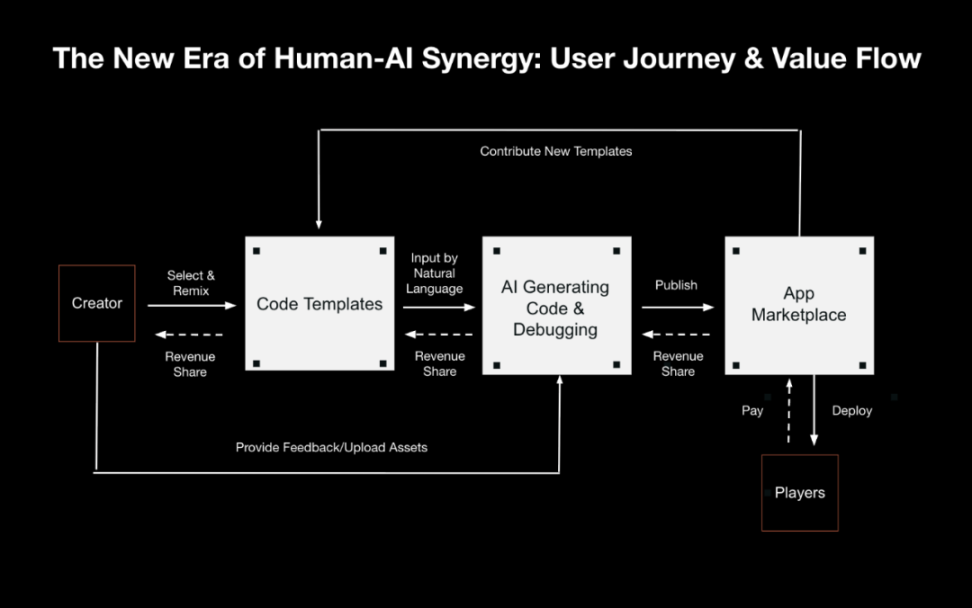
The platform currently has built-in templates for multiple lightweight Web3 applications, including NFT marketplaces, DAO management, on-chain data dashboards, RWA registration forms, content subscription systems, etc., covering common creative, community, and trading scenarios. Users can call, modify, or completely reconstruct the structure based on new semantics as needed. All building steps are completed within the platform, further forming a new chain process from Prompt to module combination to publishing and running.

It is worth mentioning that the Infinity Ground platform has now connected more than 17.41 million unique wallet addresses and generated more than 136,000 online applications, forming a relatively significant user scale. Its user profile mainly covers market operators, NFT and Meme creators, independent product managers, students, and Web3 players. The platform has also incubated representative products such as the on-chain AI Town game "Love Terminal" (attracting more than 58,000 users in the first week) and the on-chain mini-game "Jump Jennie" (completing more than $16,000 in entry fees within two weeks), fully verifying the commercial realization potential of Infinity Ground.
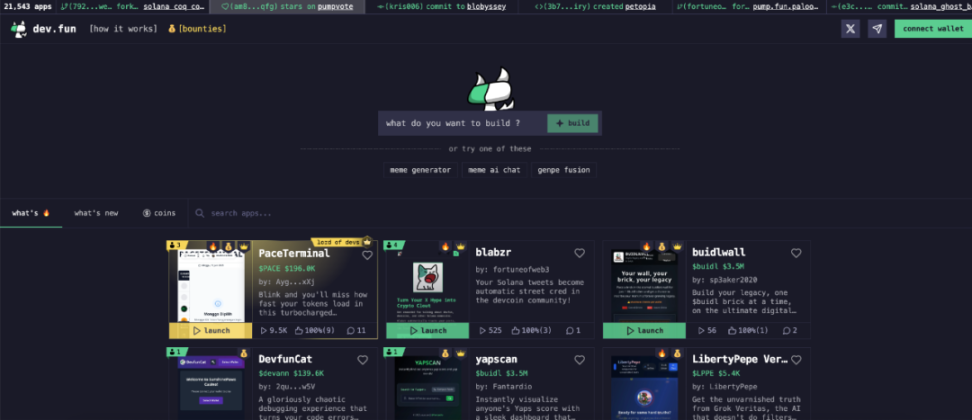
- Dev.fun
Dev.fun is a tool-type platform in the Vibe Coding track that emphasizes "light expression" and "instant interaction." Based on a minimalist semantic input mechanism, it allows users to quickly generate interactive module pages (called devlet) with preliminary logic through a single natural language sentence, without programming or configuration. Common applications include voting, mini-games, forms, real-time displays, etc., emphasizing low creation threshold and short distribution path.
The platform has a large amount of template content generated or remixed by users, supporting direct generation of access links for community sharing or embedded dissemination, building a content dissemination path with Meme characteristics. Dev.fun also provides mechanisms such as likes, leaderboards, and creative challenges to encourage expression creation around hot topics and community discussions.
In terms of positioning, Dev.fun is more like a Meme engine for Web3 community culture. It serves content creators, community operators, and brand expressers, making "building is expression" a normal way of creation. By connecting users with lightweight interactive content and amplifying influence, it is a representative expressive platform in Vibe Coding.
- Ohara AI
Ohara AI is one of the representative platforms in the Vibe Coding track focusing on "building + incentives," dedicated to building runnable Web3 applications through natural language and automatically issuing exclusive App Coins to support incentives, trading, and community interaction.
The platform provides a modular conversational building experience. Users only need to input requirements, such as "create a Meme tool that can generate GIFs" or "build a button that supports ETH donations," and the system can generate a complete application including front-end pages, wallet interaction, and on-chain calls. Applications can run instantly, be semantically fine-tuned, and allow users to access the underlying code for secondary editing.
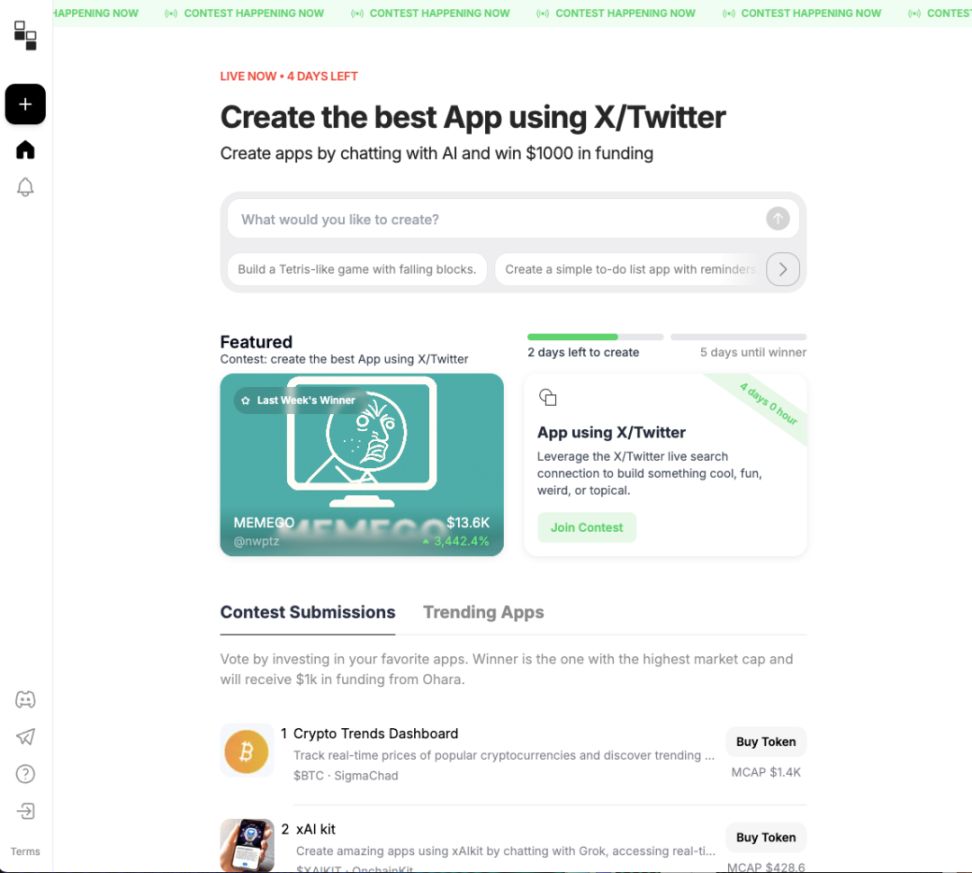
Ohara AI's biggest feature is "one-click deployment + automatic App Coin generation." Each application can embed a token incentive mechanism for tipping, distribution, or sales, realizing an economic closed loop between creators and users. The platform also supports Remix building, making it easy to quickly copy, modify, and publish applications, promoting community co-creation.
Ohara has a built-in OnchainKit SDK, supporting wallet access, on-chain operations, data reading, and can connect to external APIs, such as integrating xAI or real-time content sources, enhancing application interactivity. The platform also regularly holds development challenges to enhance user participation and content exposure. Currently, Ohara's user base includes creators, entrepreneurs, and Web3 content experimenters, suitable for rapid prototype testing and token mechanism verification, making it an ideal platform for lightweight developers and creative product validators.
Diverse Evolution Paths of Vibe Coding
In fact, the three platforms represent different verticals.
Among them, Infinity Ground takes the "closed loop of Web3 application generation, deployment, and distribution" as its core design concept. Its system builds a complete end-to-end generative infrastructure around Prompt generation, module invocation, on-chain deployment, wallet interaction, permission configuration, and application distribution, emphasizing a complete product path from "creation" to "usable and shareable," leveraging the combined capabilities of template ecosystem, runtime environment, and deployment support.
Ohara AI is more like a "front-end prototype generation tool." Its core capability is mainly focused on generating page sketches through natural language descriptions, supporting simple interactions and static display content. Ohara AI's "generate and display" path is closer to the thinking of Web2 creation tools and is also suitable for educational scenarios and creative expression. It is more like a "starter generator" or "prototype drafter" in the Vibe Coding track.
Dev.fun is positioned between the two. Its target users are mainly Meme creators and on-chain content builders, supporting the generation of visually expressive content pages from text intentions, while providing basic wallet connection and data interface calling functions, combining lightweight semantic interaction and template-driven, emphasizing "quickly making shareable works," and is more like a tool-type platform for creator communities.
If we roughly summarize Vibe Coding into two types of paths:
One type will be system platforms with infrastructure attributes, attempting to reshape the entire process of "building—deployment—distribution";
The other type focuses on specific links, targeting lightweight generation, creative display, or front-end sketches, forming a group of tool-type or Launchpad-type platforms.
Under this framework, Infinity Ground is closer to the former. Its system builds a complete closed loop around the building process, runtime environment, and distribution mechanism. Based on natural language generation of functional structures, it also has built-in on-chain deployment, wallet binding, permission settings, and application template ecosystem, with high reusability and scalability. With the vision of "Web3 App Store," it essentially belongs to the infrastructure-type project in the Vibe Coding track, aiming to serve the creator community and precipitate the module market.
According to the technical fundamentals of Infinity Ground, it is being classified as L3+ intelligent level, and performs outstandingly in terms of visibility, Web3 nativeness, composability, and ease of use, demonstrating the platform's systematic capability in building a complete ecological closed loop.
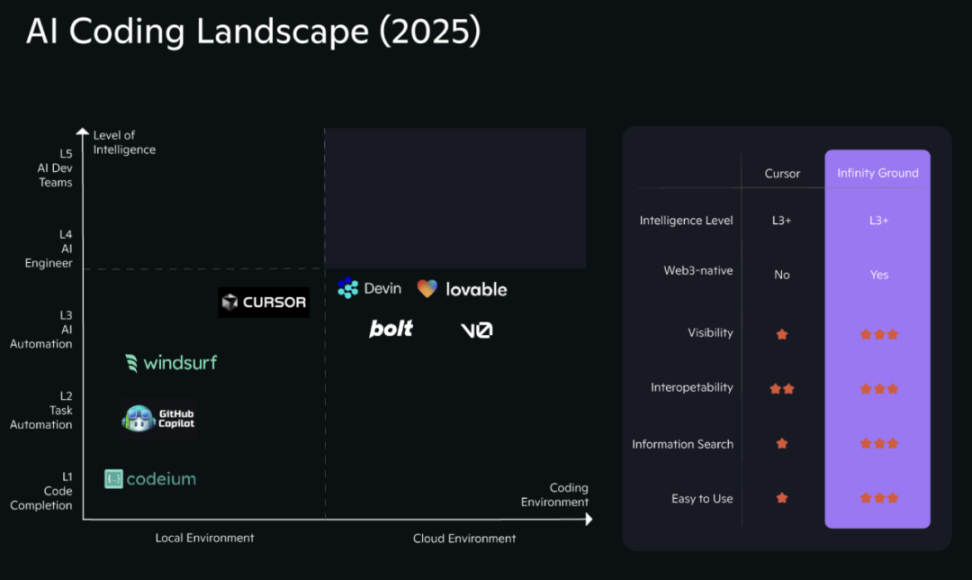
In terms of functional structure, further horizontal comparison also verifies the above differentiation path.
As shown in the table below, Infinity Ground supports the generation of multi-page structures, stable wallet connection, real-time on-chain data display, and AI collaborative generation under user intention participation, with strong system combination capabilities and full-chain orientation. Ohara AI and Dev.fun, although each has its highlights, are more focused on front-end sketches, creative content generation, and basic on-chain interaction directions.

In summary, the current Vibe Coding ecosystem has initially formed two evolutionary paths: "infrastructure-type platforms" and "tool-type generators." Infinity Ground, as a representative of the former, demonstrates systematic closed-loop advantages in building logic, operation path, and ecological organization capability, while Ohara AI and Dev.fun are more Launchpad-oriented, positioned as entry tools for lightweight building. This differentiation trend also marks that Vibe Coding is evolving from a single building tool to a multi-level, multi-role system.
Conclusion
Vibe Coding is at an early stage where technological evolution and user cognition are improving simultaneously. As the capabilities of large models continue to be released and the demand for Web3 native building continues to grow, "language as building" is gradually becoming the mainstream paradigm for next-generation application development, opening the underlying entrance to the era of "development for all."
Based on this, user identities are undergoing structural changes, extending from programmers to creators, operators, educators, and even individual entrepreneurs. The high-threshold process originally belonging to technical experts is being reconstructed into a more universal, expressive, and operable building path. This lowering of the threshold not only brings broad user growth space but also significantly expands the potential market size of the track.
Currently, the track is flourishing. Whether it is end-to-end platform-type products represented by Infinity Ground, or lighter-weight building tools such as Dev.fun and Ohara AI, although their service targets and functional focuses are different, they are all deeply exploring the core proposition of "low-threshold building." They are not simply homogeneous competitors, but are jointly expanding application boundaries and achieving complementary penetration in different verticals.
From an industry perspective, Vibe Coding has the typical characteristics of platform innovation. Once its underlying logic gradually stabilizes, the composability of modules and the scalability of the ecosystem will continue to unleash potential, and it is expected to form a development stack structure similar to an operating system, thereby reshaping the entire cycle path from product conception to validation, from iteration to launch.
In summary, Vibe Coding is an early-stage track with clear structural growth, multi-scenario scalability, and strong platform moat potential. What it drives is not only the evolution of development tools, but also a redistribution of building rights and a universal release of creativity. In the next 3 to 5 years, as the ecosystem improves and user awareness matures, this field is expected to become one of the most promising long-term opportunity windows at the intersection of AI and Web3.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Analyst: XRP Price Could Drop to $0.79. Here’s Why

'Bitcoin Senator' Cynthia Lummis Will Not Run for Reelection
Pi Network Price Prediction 2026-2030: The Shocking Truth Behind Pi Coin’s Drop
