Macroeconomic Interpretation: Powell's "Driving in the Fog" and the Financial "Hunger Games"
The article discusses the uncertainty in the global economy under the Federal Reserve's policies, particularly Powell's "hawkish rate cuts" and their impact on the market. It analyzes market distortions driven by liquidity, the capital expenditure risks of the AI investment boom, and the loss of trust caused by policy centralization. Finally, the article provides updates on macroeconomic indicators and market trends. Summary generated by Mars AI. This summary is generated by the Mars AI model, and the accuracy and completeness of its content are still in the process of iterative improvement.
Original Title: "Driving in Fog” and the Financial Hunger Games
Original Author: @arndxt_xo
Translated by: Dingdang, Odaily
The sharp correction coincides with the quantitative easing (QE) cycle—when the Federal Reserve intentionally extends the maturity of its asset holdings to lower long-term yields (an operation known as “Operation Twist” as well as QE2/QE3).
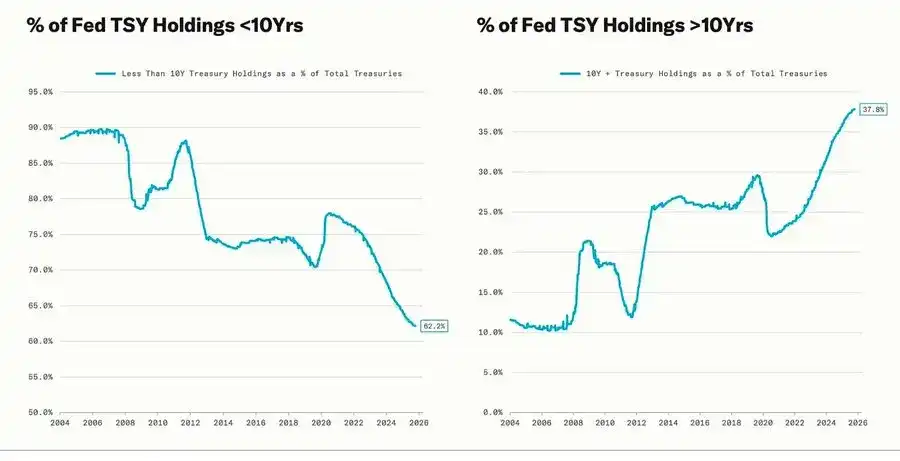
Powell’s “driving in fog” metaphor is no longer limited to the Federal Reserve itself, but has become a portrayal of today’s global economy. Whether policymakers, businesses, or investors, all are groping forward in an environment lacking clear visibility, relying only on liquidity reflexes and short-term incentive mechanisms.
The new policy regime presents three characteristics: limited visibility, fragile confidence, and liquidity-driven distortions.
The Fed’s “Hawkish Rate Cut”
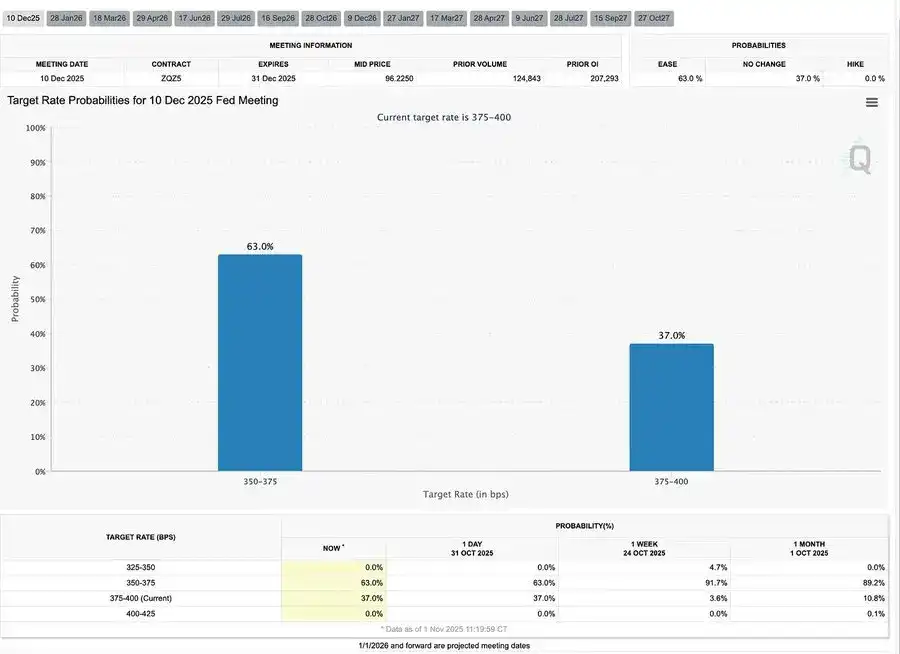
This 25 basis point “risk management” rate cut, lowering the rate range to 3.75%–4.00%, is less about easing and more about “preserving optionality.”
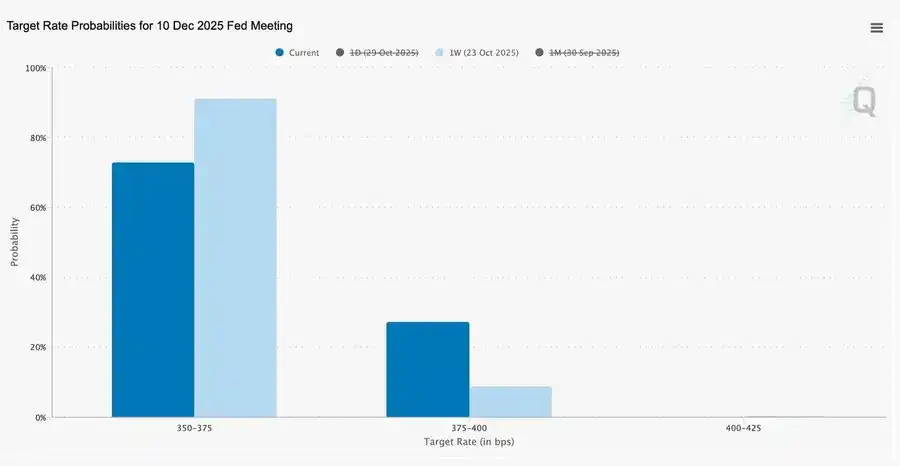
Due to two sharply opposing views, Powell sent a clear signal to the market: “Slow down—the visibility is gone.”
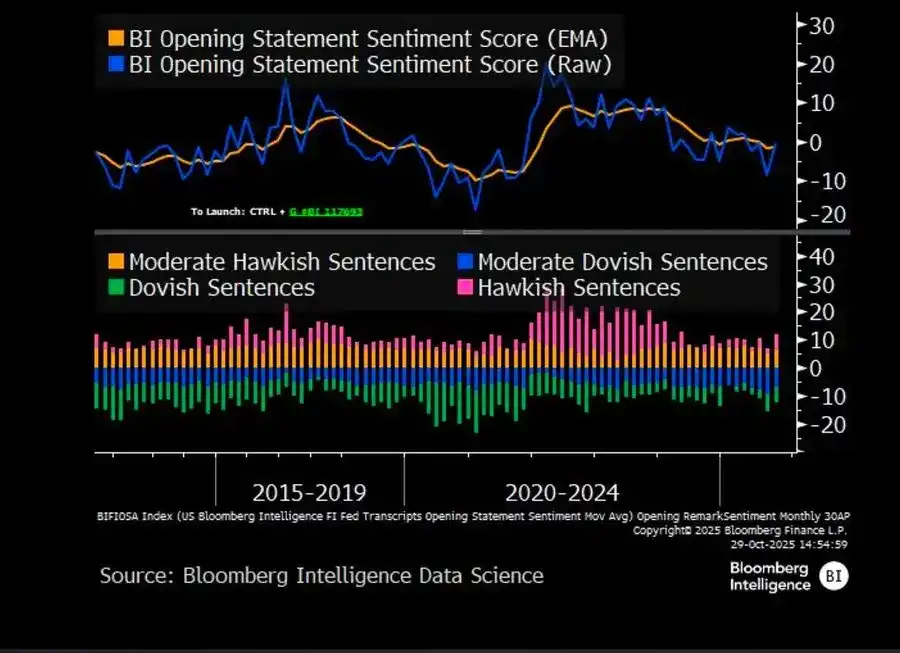
Due to a data blackout caused by a government shutdown, the Fed is almost “driving blind.” Powell’s hint to traders was very clear: Whether rates will be announced in December is still undecided. Rate cut expectations quickly receded, the short end of the yield curve flattened, and the market is digesting a shift from “data-driven” to “data-missing” caution.
2025: The Liquidity “Hunger Games”
Repeated central bank interventions have institutionalized speculation. Now, what determines asset performance is not productivity, but liquidity itself—this structure leads to ever-expanding valuations while credit to the real economy weakens.
The discussion further extends to a sober examination of the current financial system: passive concentration, algorithmic reflexivity, retail options frenzy—
- Passive funds and quantitative strategies dominate liquidity, volatility is determined by positioning, not fundamentals.
- Retail call option buying and Gamma squeezes create synthetic price momentum in the “Meme sector,” while institutional funds crowd into an ever-narrower group of market leaders.
- The host calls this phenomenon the “financial version of the Hunger Games”—a system shaped by structural inequality and policy reflexivity, forcing small investors toward speculative survivalism.
2026 Outlook: The Boom and Worries of Capital Expenditure
The AI investment wave is pushing “Big Tech” into a post-cyclical industrialization phase—currently driven by liquidity, but facing leverage sensitivity risks in the future.
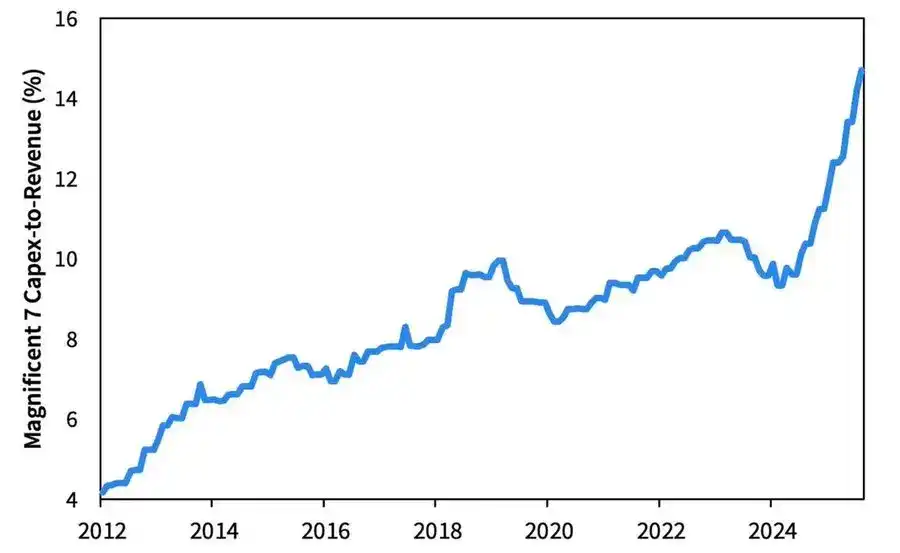
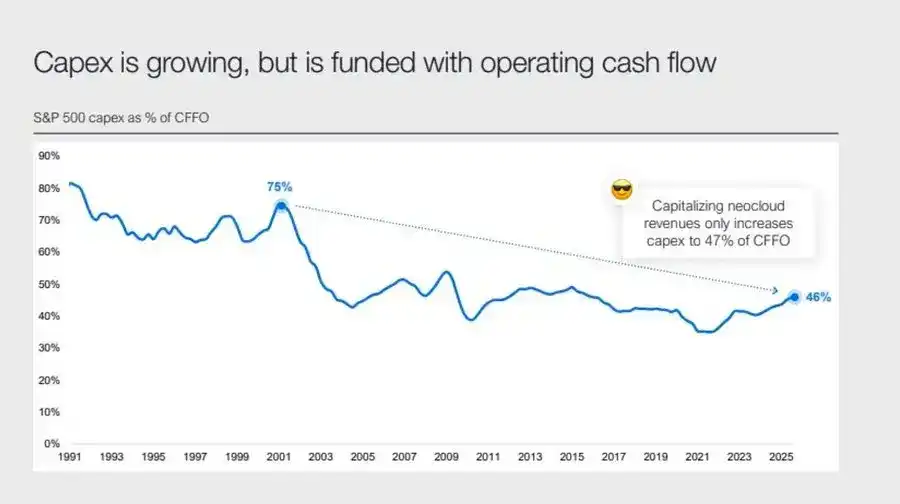
Corporate profits remain impressive, but the underlying logic is changing: the former “asset-light cash machines” are transforming into heavy capital infrastructure players.
- The expansion of AI and data centers initially relied on cash flow, but now turns to record-breaking debt financing—for example, Meta’s oversubscribed $25 billion bond issue.
- This shift means margin compression, rising depreciation, and increased refinancing risk—setting the stage for the next credit cycle reversal.
Structural Commentary: Trust, Distribution, and Policy Cycles
From Powell’s cautious tone to the final reflection, a clear thread runs throughout: power concentration and loss of trust.
Every policy bailout almost always strengthens the largest market participants, further concentrating wealth and continuously undermining market integrity. The coordinated operations of the Fed and the Treasury—from quantitative tightening (QT) to short-term Treasury bill purchases—exacerbate this trend: liquidity is abundant at the top of the pyramid, while ordinary households are suffocated by stagnant wages and rising debt.
Today, the core macro risk is no longer inflation, but institutional fatigue. The market surface remains prosperous, but trust in “fairness and transparency” is eroding—this is the true systemic fragility of the 2020s.
Macro Weekly Report | Updated November 2, 2025
This issue covers the following:
- This week’s macro events
- Bitcoin heat indicators
- Market overview
- Key economic indicators
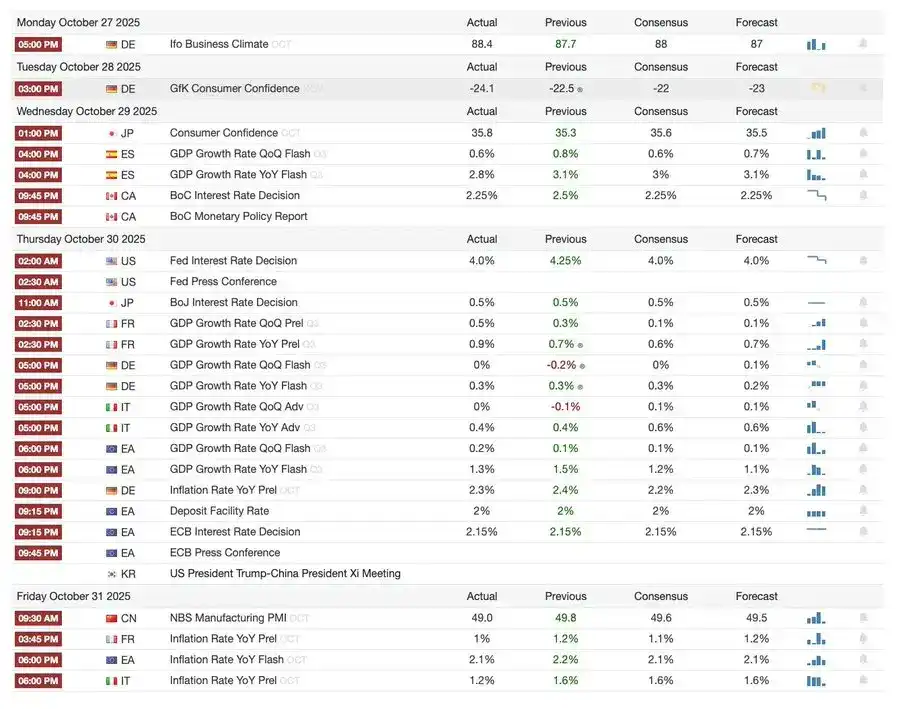
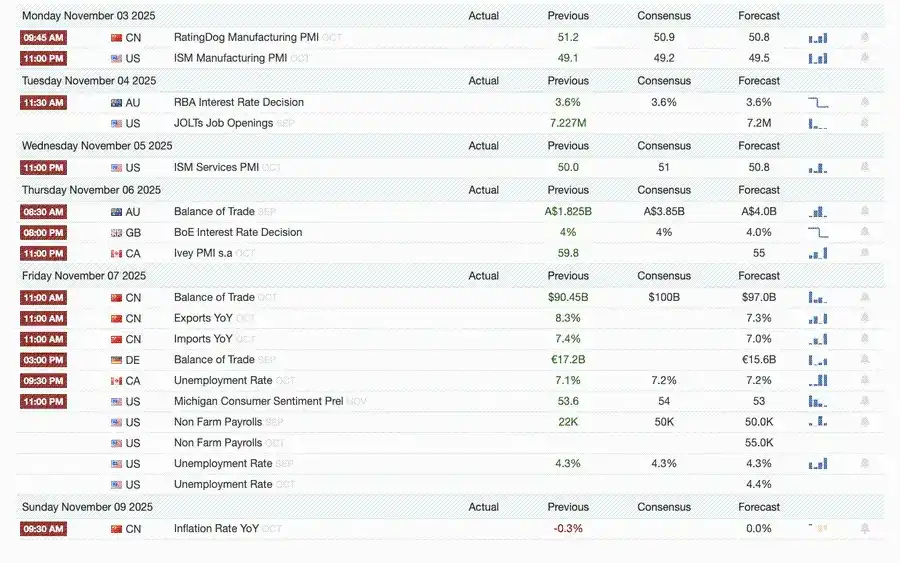
This Week’s Macro Events
Last week
Next week

Bitcoin Heat Indicators
Market Events and Institutional Developments
- Mt. Gox extends repayment deadline to 2026, about $4 billion in bitcoin remains frozen.
- Bitwise Solana ETF reached $338.9 million in AUM in its first week, setting a new record, even as the SEC remains in an approval deadlock.
- ConsenSys plans to IPO in 2026, with underwriters including JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs, targeting a $7 billion valuation.
- Trump Media Group launches Truth Predict—the first prediction market co-developed by a social media platform and Crypto.com.
Financial and Payment Infrastructure Upgrades
- Mastercard acquires crypto infrastructure startup Zerohash for up to $2 billion.
- Western Union plans to launch the stablecoin USDPT on Solana in 2026 and registers the WUUSD trademark.
- Citi and Coinbase jointly launch an institutional-grade 24/7 stablecoin payment network.
- Circle launches Arc public testnet, attracting participation from over 100 institutions including BlackRock and Visa.
Ecosystem and Platform Expansion
- MetaMask launches multi-chain accounts, supporting EVM, Solana, and soon to add bitcoin support.
Global and Regional Developments
- Kyrgyzstan launches a stablecoin backed by BNB; meanwhile, Trump pardons CZ, paving the way for Binance’s return to the US market.
- US SOL spot ETF (excluding seed capital) sees $199.2 million in inflows.
- Japan launches fully compliant yen stablecoin JPYC, targeting an issuance scale of $65–70 billion by 2028.
- Ant Group registers the “ANTCOIN” trademark, quietly returning to the Hong Kong stablecoin track.
- AWS and Microsoft cloud service outages cause market chaos, with conflicting statements from both sides.
- JPMorgan Kinexys blockchain completes its first tokenized private equity fund transaction, further promoting institutional adoption.
- Tether becomes one of the largest US Treasury holders, with holdings reaching $135 billion and annualized returns exceeding $10 billion.
- Metaplanet launches a stock buyback plan to address declining net assets.
- Privacy asset trading heats up, ZEC price breaks 2021 highs, but this week’s gains still lag behind DASH.
- Sharplink deploys $200 million ETH on Linea to capture DeFi yields.
- With sports betting becoming a hot sector, Polymarket plans to officially launch in the US by the end of November.
- Securitize announces a $1.25 billion SPAC merger to go public.
- Visa adds payment support for four new stablecoins and four new chains.
- 21Shares files for Hyperliquid ETF, with more crypto funds entering the market.
- KRWQ becomes the first Korean won stablecoin issued on the Base chain.
Market Overview
The global economy is shifting from inflation risk to confidence risk—future stability will depend on policy clarity, not liquidity.
Global monetary policy is entering a phase of limited visibility. In the US, the FOMC cut rates by 25 basis points to 3.75%–4.00%, exposing widening internal divisions. Powell hinted that further easing in the future is “not a given.” The ongoing government shutdown prevents policymakers from accessing key data, increasing the risk of policy misjudgment. Weakening consumer confidence and a slowing real estate market mean that market sentiment, rather than stimulus measures, is now steering the path of economic “soft landing.”
Among G10 countries: the Bank of Canada completed its final rate cut, the European Central Bank kept rates unchanged at 2.00%, and the Bank of Japan paused cautiously. The common challenge is: how to curb economic growth amid persistent service sector inflation. Meanwhile, China’s PMI has slipped back into contraction, showing weak recovery, sluggish private demand, and signs of policy fatigue.
Adding political risk, the US government shutdown threatens the normal operation of welfare programs and may delay the release of key data, undermining confidence in fiscal governance. The bond market has already begun to price in lower yields and slower economic growth, but the real risk lies in the breakdown of institutional feedback mechanisms—data delays, policy hesitation, and declining public trust intertwine, ultimately brewing a crisis.
Key Economic Indicators
US Inflation: Moderate Rebound, Clearer Path
The inflation rebound is mainly supply-driven, not demand-pulled. Core pressures remain under control, and weakening employment momentum gives the Fed room to continue cutting rates without triggering an inflation rebound.
- September inflation was up 3.0% year-on-year and 0.3% month-on-month, the fastest since January this year, but still below expectations, reinforcing the “soft landing” narrative.
- Core CPI excluding food and energy was up 3.0% year-on-year and 0.2% month-on-month, showing price stability.
- Food prices rose 2.7%, with meat up 8.5%, affected by agricultural labor shortages due to immigration restrictions.
- Utility costs rose significantly: electricity +5.1%, natural gas +11.7%, mainly driven by AI data center energy consumption—a new driver of inflation.
- Service sector inflation fell to 3.6%, the lowest since 2021, indicating that a cooling labor market is easing wage pressures.
- Market reaction was positive: stocks rose, interest rate futures reinforced rate cut expectations, and bond yields remained stable overall.
US Demographics: A Critical Turning Point
Net immigration turns negative, posing challenges for economic growth, labor supply, and innovation capacity.
The US may face its first population decline in a century. Although births still outnumber deaths, net immigration is negative, offsetting the 3 million population increase in 2024. The US is facing a demographic reversal, not due to falling birth rates, but due to policy-driven declines in immigration. Short-term impacts include labor shortages and rising wages; long-term risks focus on fiscal pressure and slowing innovation. Unless this trend is reversed, the US may repeat Japan’s aging experience—slowing economic growth, rising costs, and facing structural productivity challenges.
According to AEI forecasts, net migration in 2025 will be –525,000, the first negative value in modern history.
- Pew Research Center data shows that in the first half of 2025, the foreign-born population fell by 1.5 million, mainly due to deportations and voluntary departures.
- Labor force growth stagnates, with agriculture, construction, and healthcare facing obvious shortages and wage pressures.
- 28% of American youth are immigrants or children of immigrants; if immigration drops to zero, the under-18 population may fall by 14% by 2035, increasing pension and healthcare burdens.
- 27% of doctors and 22% of nursing assistants are immigrants; if supply drops, automation and robotics in healthcare may accelerate.
- Innovation risk: immigrants have contributed 38% of Nobel Prizes and about 50% of billion-dollar startups; if the trend reverses, America’s innovation engine will be damaged.
Japan Export Recovery: Rebound Under the Shadow of Tariffs
Despite being dragged down by US tariffs, Japan’s exports have rebounded. September exports rose 4.2% year-on-year, the first positive growth since April, mainly due to reviving demand in Asia and Europe.
After months of contraction, Japan’s exports returned to growth, up 4.2% year-on-year in September, the largest increase since March. This rebound highlights that despite new trade frictions with the US, regional demand remains strong and supply chains have adjusted accordingly.
Japan’s trade performance shows that, despite US tariffs on automobiles (its core export category), external demand from Asia and Europe has initially stabilized. The rebound in imports indicates that, driven by a weaker yen and restocking cycles, domestic demand is also seeing a mild recovery.
Outlook:
- Exports are expected to gradually recover, driven by normalization of intra-Asia supply chains and energy prices.
- Persistent US protectionism remains the main obstacle to maintaining export momentum through 2026.
Recommended Reading:
$1 billion stablecoin evaporates, what’s the truth behind the DeFi domino collapse?
MMT short squeeze review: a carefully designed money-grabbing game
Under brutal harvesting, who is looking forward to the next COAI?
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Ethereum faces tough path to $3.9K as sentiment and demand fizzle

Can Bitcoin bulls avoid the cycle’s fourth ‘death cross’ at $102K?

Technical Traceability Analysis Report on the LuBian Mining Pool Hacked and Massive Bitcoin Theft Incident
The US government may have already used hacking techniques as early as 2020 to steal 127,000 bitcoins owned by Chen Zhi. This is a typical "black eats black" incident orchestrated by a state-level hacker organization. This report takes a technical perspective, conducting technical tracing to deeply analyze the key technical details of the incident, focusing on the ins and outs of the theft of this batch of bitcoins, reconstructing the complete attack timeline, and evaluating the security mechanisms of bitcoin. The aim is to provide valuable security insights for the cryptocurrency industry and its users.

